2024
AKIS coordination bodies
governance
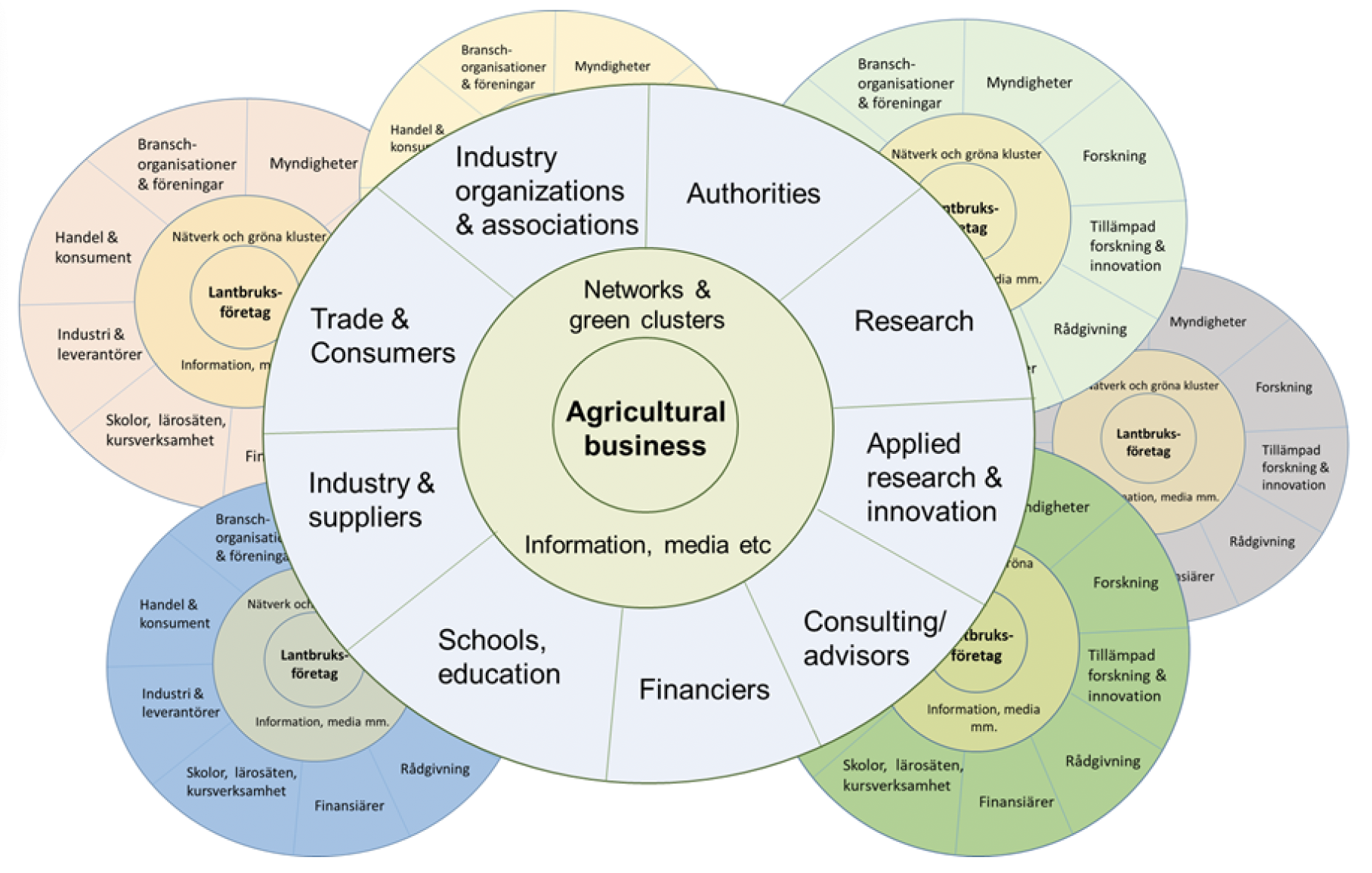
The Swedish Agricultural Knowledge and Innovation Systems (AKIS) encompasses a wide range of actors, expertise, and collaborative efforts (figure 1). However, the current structure has room for improvement and enhancement to better align with the needs of businesses and expand their ability to engage in competitive and commercial activities. Both the CAP and national initiatives can play a key role in fostering stronger cooperation between fundamental research, applied research, industry, and advisory services, facilitating greater knowledge exchange, innovation, and digitalisation.
Similarly, the Forestry Knowledge and Innovation Systems involves numerous actors, including major public entities like the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU), the Swedish Forest Agency, and the research institute Skogforsk. Skogforsk, which is co-funded by forestry companies, works to develop and disseminate knowledge, services, and products that support sustainable forestry practices for the benefit of society.
Alongside the ongoing investments in research and innovation, there is a strong focus on better integrating the food sector into broader national and regional innovation ecosystems, fostering synergies and creating new networks. Moreover, the European Innovation Partnership (EIP) and collaborative initiatives are being reinforced to further drive innovation in environmental sustainability and agricultural production.
To improve collaboration and knowledge sharing four knowledge hubs were set up about i) livestock production, ii) business management and entrepreneurship, iii) environment and climate, iv) digitalisation. They act as impartial knowledge centers aimed at bridging research and practice. They serve as hubs for the compilation and dissemination of valuable insights, facilitating knowledge exchange among stakeholders. Particularly, the key objectives of the hubs are:
The political relevance given to AKIS strategies in the context of the CAP Strategic Plans (SPs) 2023-2027 has certainly highlighted the opportunity of defining governance bodies aimed at coordinating the AKIS-relating interventions and actors in view of their better implementation and contribution to the cross-cutting and specific objectives of the CAP SPs.
Particularly, the AKIS coordination body is indicated by the CAP SP 2023-2027 as a point of contact of the European Commission and of the European CAP Network.
For the constitution of the Swedish AKIS CB, it has been given great importance to the needs gathered from the sector, the analyses carried out and the conclusions drawn from these. Swedish AKIS coordination is therefore largely needs-oriented, with the aim of coordinating activities, efforts and knowledge development to facilitate the actors involved in the Swedish knowledge and innovation systems for agriculture.
The coordination of AKIS is carried out in cooperation between the Swedish Board of Agriculture (box 1) and the Swedish CAP Network (box 2). The basis of the function consists of different responsibilities and roles that the Board of Agriculture and the network currently have.
Figure 2: Swedish AKIS Coordination Body
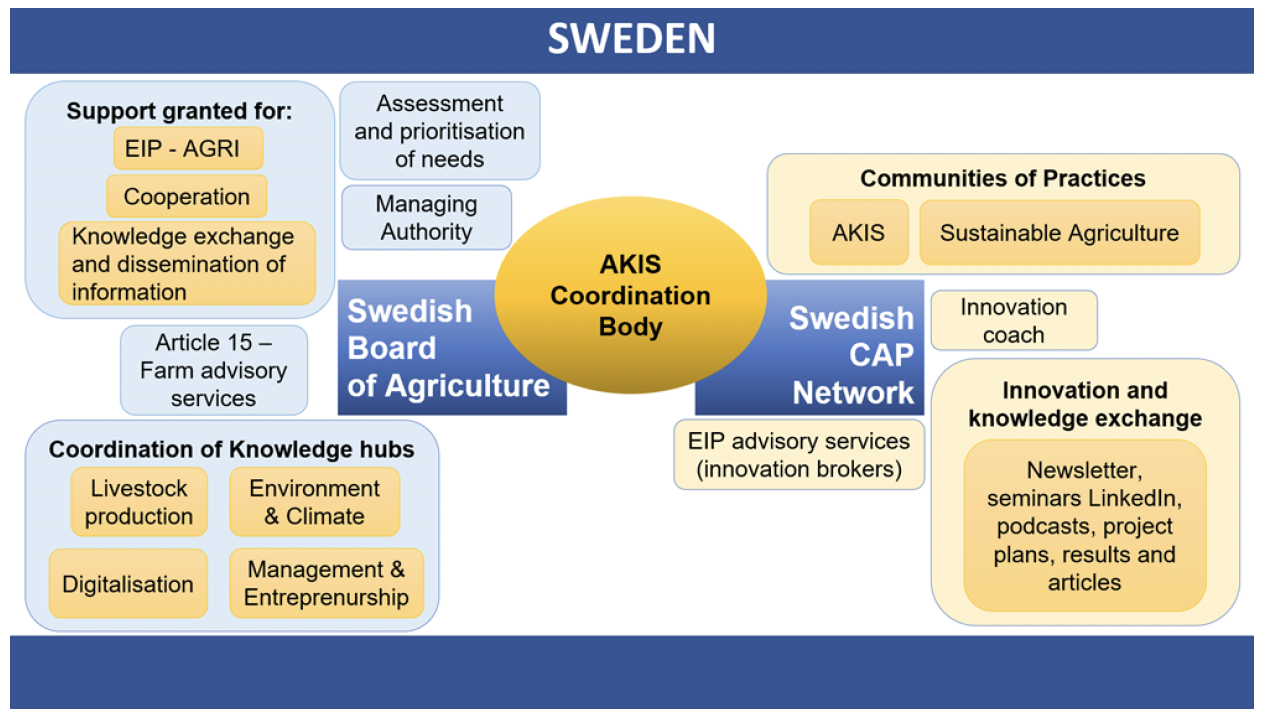
Source: Swedish Board of Agriculture (2024)
Box1: Swedish Board of Agriculture
The Swedish CAP Network brings together organisations from civil society, business, consultancy, research and education as well as authorities to learn from each other and collaborate. In this way, they contribute to the goals of agriculture, fishing and aquaculture as well as rural development while creating added value for them and their own organizations. The Network is part of the European CAP Network and can therefore also learn from and collaborate with colleagues around Europe.
The steering group consists of 15 members and a chairman, who all represent different key players and members in the Network. They prioritise themes and resources based on the wishes of the member organisations. The steering group is also responsible for following up to ensure that the network delivers the expected results.
One of the Network's member organisations is the Swedish Association of Local Authorities and Regions. There has been regional representation in several of the operating groups.Source: Swedish Board of Agriculture website
Box2: Swedish CAP NetworkThe Swedish CAP Network brings together organisations from civil society, business, consultancy, research and education as well as authorities to learn from each other and collaborate. In this way, they contribute to the goals of agriculture, fishing and aquaculture as well as rural development while creating added value for them and their own organisations. The Network is part of the European CAP Network and can therefore also learn from and collaborate with colleagues around Europe.
The steering group consists of 15 members and a chairman, who all represent different key players and members in the Network. They prioritise themes and resources based on the wishes of the member organisations. The steering group is also responsible for following up to ensure that the network delivers the expected results.
One of the Network's member organisations is the Swedish Association of Local Authorities and Regions. There has been regional representation in several of the operating groups.
Source: Swedish Board of Agriculture website
The functions assigned to AKIS CB are:
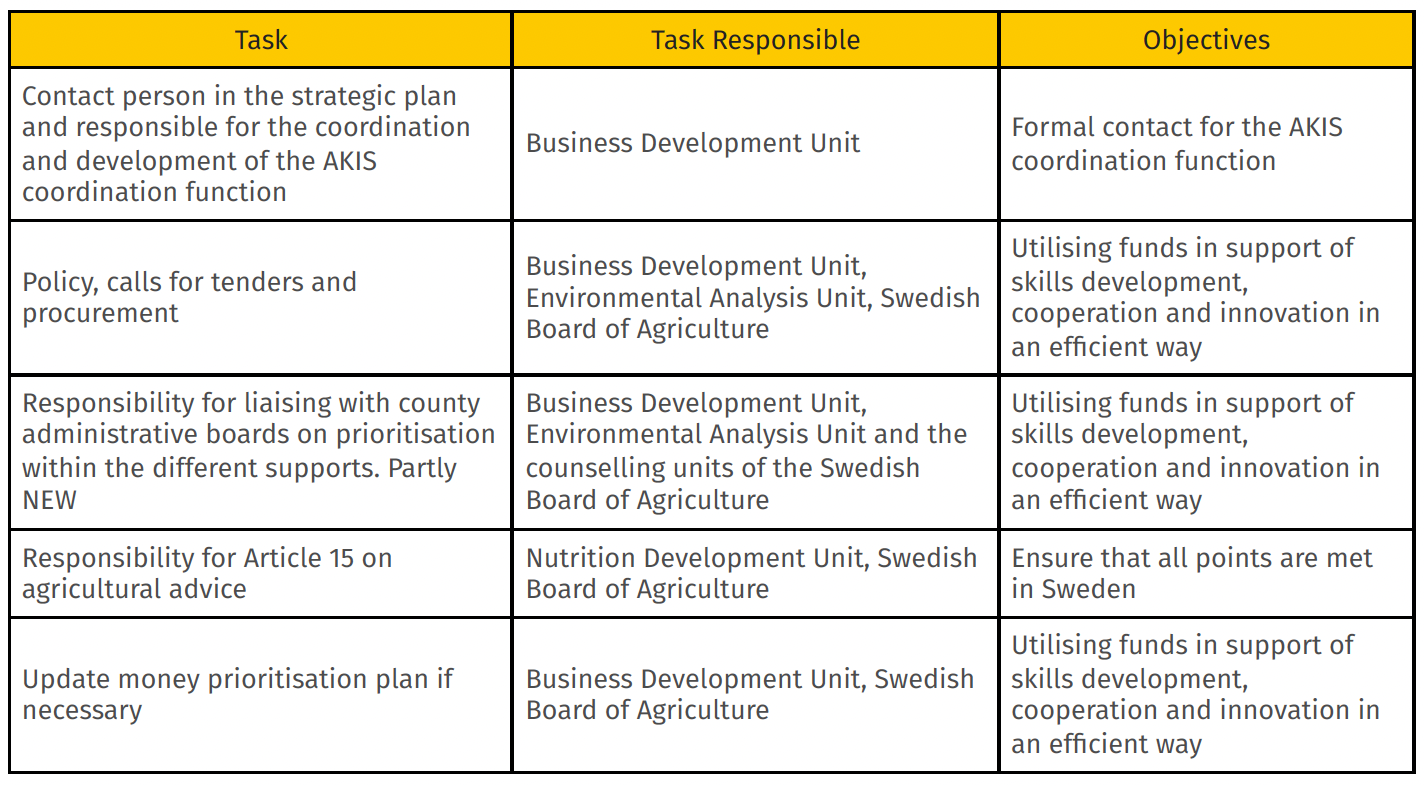
The purpose of the AKIS coordination body is largely to coordinate activities, efforts and knowledge development to facilitate actors involved in the Swedish knowledge and innovation systems for agriculture. For this reason, the Swedish AKIS coordination body performs several functions (Table 1).
Particularly, the Swedish Board of Agriculture has so-called policy officers who are responsible, among other things, for liaising with the European Commission and driving changes in the strategic plan with regard to the subsidies. Several units are allocated budgets within the support programmes and are then responsible for calls for proposals and procurements within that budget.
For units with responsibility for policy and budget for the support, this includes, for example, following and supporting the county administrative boards' work with this support.
The Swedish Board of Agriculture also has an important role in providing adviser training and conducting development work of relevance to the supply of knowledge, primarily in agricultural environmental issues, this is part of the work to create conditions for which the advisory units at the Swedish Board of Agriculture are responsible. Moreover, the Swedish Board of Agriculture is responsible for ensuring that all points of Article 15 of EU Regulation on agricultural advisory services are fulfilled in Sweden.
On the other hand, the CAP Network performs functions of innovation coach (especially in the knowledge and innovation promotion in green industries) and innovation support for anyone interested in applying for EIP-Agri innovation interventions.
Table 1: Tasks of the AKIS coordination
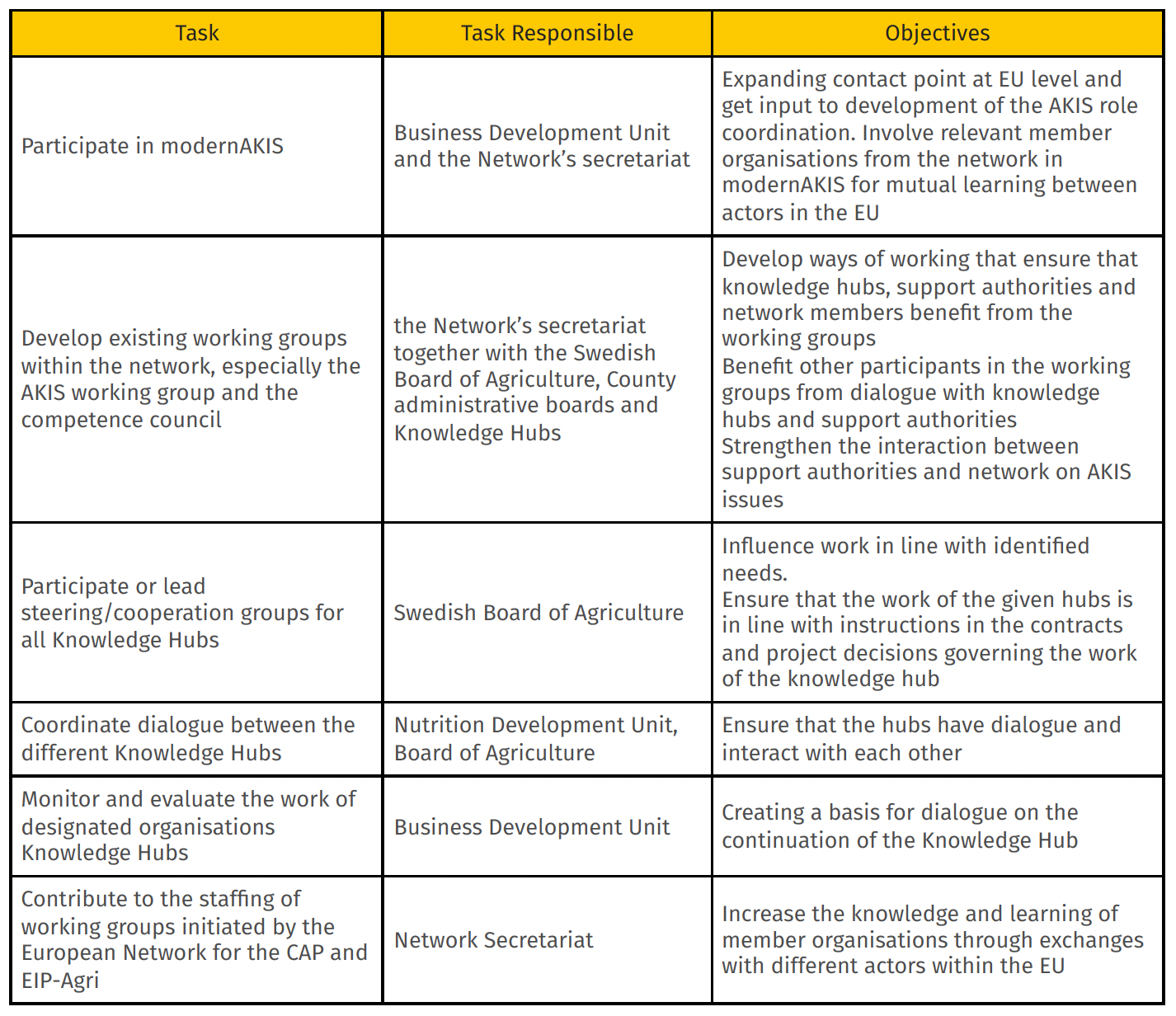
In addition to developing collaboration between the Swedish Board of Agriculture and the Swedish CAP Network within the AKIS coordination function the Swedish AKIS CB has defined a development plan intended to be continuously updated, evaluated and developed according to the needs of the industry, and in collaboration with Swedish AKIS actors - where other support authorities are also included.
Particularly the AKIS Coordination Body works on:
The Swedish CAP network's main mission is to provide value for its members. For example, the two AKIS CoPs coordinated by the Swedish CAP Network as well as many other networking, innovation building and coaching activities (as described in the picture above) are provided by the network and part of the network's mission. These activities, combined with the mandate of the Swedish Board of Agriculture, make AKIS coordination of actions within Strategic Plan more effective. Moreover, Sweden's active participation in the EU project modernAKIS provides support for the development of national AKIS coordination and a continuous development of the capacities.
The composition of the AKIS CB is grounded on national entities that already perform important functions related to the coordination of AKIS actors and networking.
The functions of the AKIS coordination body are based on a specific mandate by the managing authority of the CAP Strategic plan.
Moreover, the drafting of a development plan, continuously updated, gave the opportunity to periodically monitor and evaluate the AKIS CB’s activities and improve it, to better respond to the AKIS actors’ needs.
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCIO2x7zsTH_UNGs968c9QRw